Less than a month after Microsoft decided to back OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google rolled out its own assistive AI Chatbot – Bard to counter the rising popularity of its rival. Fundamentally, Google Bard AI Search Chatbot is similar to ChatGPT but unlike ChatGPT which does not use the Internet, Bard has access to Google’s search engine.
Initially, it was available to only a group of “trusted testers” but Google expedited its public launch, officially leaving the waitlist behind. Now, it’s available for everyone to use. You can use it to write stories, compile to-do lists, or even seek travel advice.
How to use Google Bard AI search chatbot?
Bard is still labeled as an “experimental conversational AI service”. As such, it remains very much a work-in-progress kind of project in the Artificial Intelligence space and can’t be relied on to answer all your questions 100% correctly. However, it does use AI to provide human-like conversational responses when prompted by a user.
To get started on how to use Google Bard, go to the Bard homepage and sign in with your Google account.
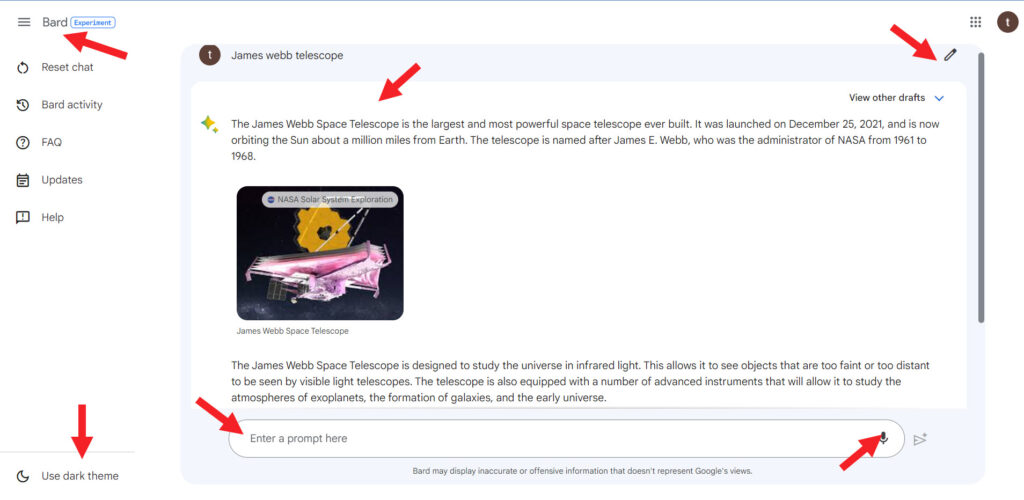
Once you get through the first step, you’ll be directed to the chat window. You’ll find it user-friendly and easy to navigate. Here’s what it includes.
1] Main Menu
It’s visible as a hamburger icon in the upper-left corner of the chat window. This menu accommodates the following options.
- Reset chat: Clears the current chat and starts a new one.
- Bard Activity: Whatever prompts you enter in the empty prompt field remain under the ‘Activity’ section. Accessing it opens a new tab with all your prompt history. You can delete the history or alternatively, turn it off. Bard does not keep a record of your conversations.
- FAQ – This section answers some of the frequently asked questions about the chatbot.
- Updates – It shows a history of the different updates rolled out for Bard AI.
- Help & Support – Provides quick access to the ‘Help & Support’ section or submit feedback related to Bard.
2] Text area
The empty test field at the bottom of the chat window lets you submit your prompts to the chatbot to see its response.
3] Microphone
Instead of typing in your prompts, you can dictate them by clicking on the microphone seen inside the empty text field.
4] Edit
Next to your prompt in the chat window, you’ll see an Edit button visible as a pencil icon. It lets gives you edit your prompt to seek a more appropriate answer, particularly useful when you want to narrow down your search without having to rewrite a new prompt.
5] Conversation
The AI-powered chatbot’s main strength is to generate multiple responses for you to review right inside its Conversation window. It appears at the center of the chat window and seeks to answer your questions through a massive dataset of text and code, including books and articles, or code and scripts.
If there’s less information available, it takes an alternative route – crawling the web via Google Search. This helps it generate new information from the so-called ‘real world’ and keep responses consistent with search results.
While submitting your prompts and receiving replies, you can hit the View other drafts button to go through other alternatives Bard comes up with. In short, you can use these drafts to get more variety in ideas for your content.
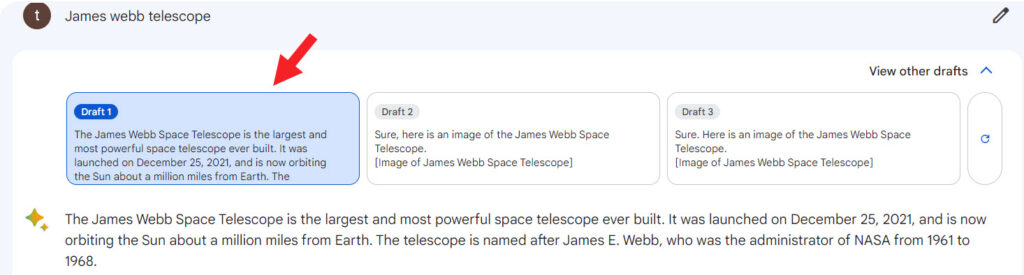
You can “Upvote” or “Downvote” a reply depending on how satisfactory the response is. Besides, underneath each response is a prominent “Google It” button that redirects users to a related Google search.
6] Dark Theme
By default, the color scheme for Bard matches the color scheme of the device you’re currently using. You can however change it and switch to the Dark theme by simply accessing the option in the lower-left corner of the main screen.
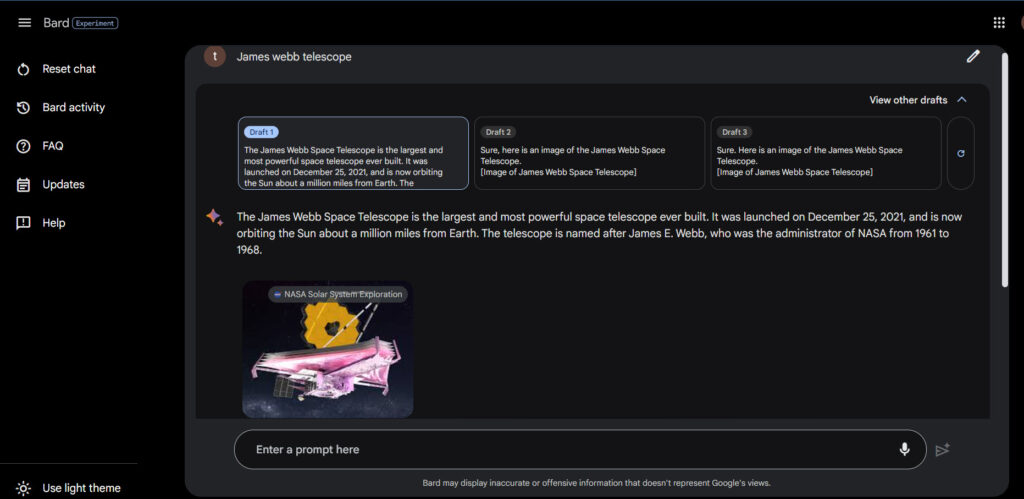
During our brief time with the utility, we found Bard did manage to quickly and fluidly answer general queries related to James Web Telescope, offering an anodyne explanation with no offensive details.
However, it has a shortfall. The AI search chatbot lacks clearly labeled footnotes as seen in Bing. They only appear in Bard when the chatbot directly quotes a source like a news article or when it seems more constrained in its answers.
For the most part, you’ll find it hard to get Bard to answer something truly vague. For example, if you ask it in a somewhat oblique way how to make explosives, Bard will turn down your request steadfastly.
Having said that, more advanced users may find Google’s offering falling short in terms of features and performance compared to its competitors, but the addition of new tools will only make it better and far more competitive. A huge new feature coming soon to Bard is the ability to create generative images from text. The feature is a collaborative effort between Google and Adobe.
For now, you can use Bard as a complimentary search experience for Google search. It’s already available in 180 countries.